Billie Eilish is perhaps the most talented artist of our generation…and I don’t throw that around lightly. At only 13, Eilish wrote “Ocean Eyes” alongside her brother Finneas and launched her prolific career. And at the fair age of 22, Eilish has 24 GRAMMY Award nominations and nine wins, two Oscars, two Golden Globes, and countless other accolades.
Beyond that, she recently announced her third album, HIT ME HARD AND SOFT, to be released May 17, 2024. She spent the days leading up to the announcement building excitement by adding all of her Instagram followers to her “Close Friends” list. Eilish had the most Instagram followers in 48 hours…with her count increasing by 7 million followers total.
While her debut album, when we all fall asleep…where do we go?, was a chart-topper in its own right, it landed Billie every GRAMMY it was nominated for at the ripe age of 18…Eilish has solidified herself as one of the most revered and sought-after popstars in the world.
Eilish recently caught media attention for quietly revealing her sexuality. In an interview with Variety, she states that she’s always liked girls…and assumed people always knew that. In a viral snippet from her new song, LUNCH, she details a love affair with a girl.
But people don’t only adore Billie for her catchy tracks that consistently top the charts. It’s not just her songwriting ability and unique vocals that keep us hooked. People love her because she’s unafraid to speak her mind.
Whether it be complaining about too many influencers being at an awards show, or calling out other artists for using unsustainable practices…Billie does not hold back.
Billie Eilish On Sustainability
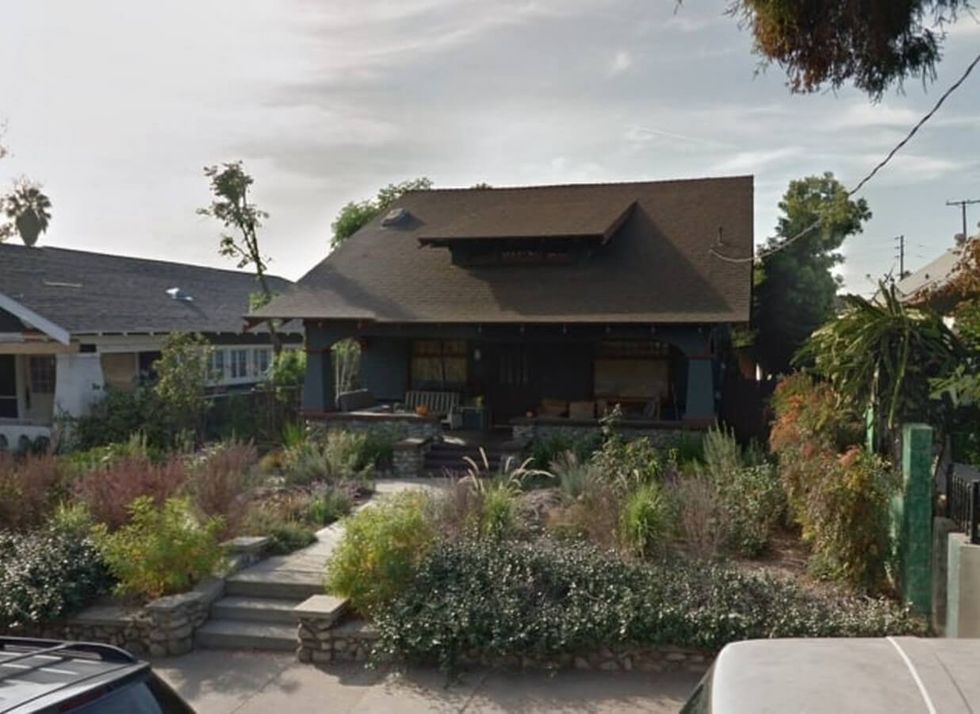

Eilish home
rethinkingthefuture.com
The Eilish home is iconic for many reasons: it’s where Billie and Finneas recorded her debut album, countless other songs, and EPs, in an effort to conserve water there’s no grass, and the roof is covered in solar panels. And being environmentally conscious extends beyond the four walls of their home.
When the hottest young talent is discovered at such an early age like Eilish, record labels are chomping at the bit to sign them. It’s like when a D1 athlete is ready to commit to college…you have your pick.
But what Eilish and her mom, Maggie Baird, were looking for wasn’t about money or label-perks…they were seeking a solid sustainability program. And while that may seem like standard practice, most labels didn’t bring up environmental policies during these meetings at all.
After signing to The Darkroom via Interscope Records, the struggle didn’t stop there. Billie Eilish and her family have been consistent contributors to the fight against climate change.
Maggie Baird has since started Support + Feed, which focuses on the climate crisis and food insecurity. Support + Feed helped Eilish’s 2022 Happier Than Ever tour save 8.8 million gallons of water through plant-based meal service for the artist and crew members.
During Billie’s 2023 Lollapalooza performance, she aided the launch and funding of REVERB’s Music Decarbonization Project – which guaranteed all battery systems used during her set were solar powered. The MCD’s overall mission is to lower – and eventually eliminate –the music industry’s carbon emissions.
But more recently, Billie Eilish called out other artists for releasing multiple versions of vinyls in order to boost vinyl sales. In an interview with Billboard, she says,
“We live in this day and age where, for some reason, it’s very important to some artists to make all sorts of different vinyl and packaging … which ups the sales and ups the numbers and gets them more money and gets them more…”
Artists convince fans to buy different versions of their albums by offering exclusive features on each vinyl. Take Taylor Swift, for example, who released five separate vinyl versions of Midnights, each with a different deluxe “Vault” track.
While Billie may not have been trying to shade one artist in particular, the point is that she’s fed up. After being the rare artist in the industry who go out of their way to remain environmentally conscious, Eilish sets the bar high.
How Eilish’s New Album Is Sustainable

Billie for "Hit Me Hard and Soft"
William Drumm
Social media users were quick to claim Eilish was hypocritical by announcing that HIT ME HARD AND SOFT will have eight vinyl variations. However, each vinyl is made from recycled materials – either 100% recycled black vinyl or BioVinyl, which replaces petroleum used during manufacturing with recycled cooking oil.
This just illustrates that Eilish wasn’t directing criticism towards other artists for using vinyl variants to gain album sales…but she does think there are better ways to do it that benefit the environment without hurting their sales.
Fortnite and Intellectual Property: Who Owns Cultural Trends?
With three high profile figures filing lawsuits against the company for marketing their likeness, the video game phenomenon is challenging who owns choreography.
Epic Games' Fortnite is at the center of controversy surrounding copyright and the limits of intellectual property laws. With three high-profile figures filing lawsuits against the company for marketing their likeness, the video game phenomenon prompts a conversation about who owns culture.
The Battle Royale style game features customizable avatars, for which users can purchase "emotes," specific gestures or dance moves that avatars can perform in the game. The problem is that "emotes" are designed to appeal to millions of international users, with many replicating wildly popular dance trends and cultural icons. Select "emotes" are based on Snoop Dogg's "Drop It Like It's Hot" dance, Psy's "Gangnam Style," and Donald Faison's "Poison" dance from the US sitcom Scrubs.

However, Fortnite's creators did not secure licenses to recreate these artists' likenesses in their game. But it's unclear under U.S. law whether or not a segment of choreography even qualifies for copyright protection. As highlighted by the Wall Street Journal, the U.S. Copyright Office's stance on choreography dictates that it "cannot register short dance routines consisting of only a few movements or steps with minor linear or spatial variations, even if a routine is novel or distinctive." They elaborate that "social dance steps and simple routines" are not protected by copyright "even if they contain a substantial amount of creative expression."
In fact, few dance moves have been successfully copyrighted. Michael Jackson was able to patent his impressive leaning move featured in the "Smooth Criminal" music video–but only because he invented the special shoe that makes it possible. Since each one of Fortnite's "emotes" is a short movement and not a creative song or dance of its own, copyright lawyers can't agree about whether or not infringement laws apply.
The first "emote" to challenge what constitutes copyright infringement is called "Swipe It," which replicates the dance move recognizable as the "Milly Rock." Its creator, rapper 2 Milly, born Terrence Ferguson, was the first to sue the game with allegations that Fortnite violates copyright law by selling his "signature" choreography. He told Rolling Stone, "My dance is my signature. Everybody would tell you, from here to Alaska, 'Hey, that's the Milly Rock.' I don't mind people doing it in their videos. What I do mind is when somebody takes what I created and sells it."
While the "Milly Rock" became a viral dance move in 2015, it isn't a full choreography set. Christine Lepera, attorney for music industry giants like Drake and Timbaland, argues that a single dance move is precluded from copyright infringement: "You cannot copyright certain dance moves that are generic. From what I've seen online, I've done these [Milly Rock] moves in hip-hop [dance] class for years — it's a pivot, heel-out, heel-out, and swing your arms."

The second creator to file charges against Epic Games is Alfonso Ribeiro, best known for playing Carlton Banks on The Fresh Prince of Bel-Air. He alleged that the "emotes" called "Fresh" plagiarizes the "Carlton Dance," made famous by the beloved sitcom character Ribeiro played in the 90s. However, copyright lawyer Scott Alan Burroughs argues that an actor doesn't own his character's stylized, or "signature," movements, since the character is owned by the production company. Burroughs says, "[Ribeiro] created and performed that dance while acting on a television show he was a performer on, so it was likely 'work for hire' that belongs to the show's producers."
The third creator to file charges against the game is the mother of Russell Horning, a 17-year-old content creator on YouTube who popularized "the floss" dance. Again, Fortnite sells a "Floss" emote that the Hornings claim infringes upon their legal right to share in the profit made through dance move.
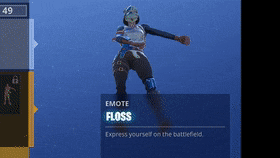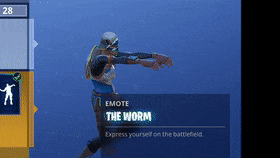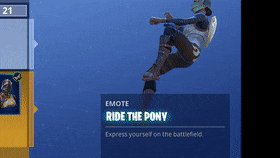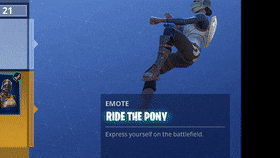
But how much money does Fortnite make from selling "emotes?" For that matter, how does a game that's technically free to play earn Epic Games over $2 billion in 2018? When the Fortnite App launched on Apple's IOS in April, the game reportedly made $2 million a day, making history as the first to net over $1 billion by following a free-to-play model.
The secret–and the root of the controversy–is the game's profit from microtransactions. While all users can play the entirety of the game for free, they have the option of purchasing in-game currency, called "V-bucks," which allows players to customize their gaming experience. With an exchange rate of approximately 1 USD to 100 V-bucks, users are offered deals to spend anywhere from $2 to $20 on cosmetic skins, game modes for their characters, and, of course, dances. Michael Pachter, an analyst at Wedbush Securities, noted, "On the revenue side, [Fortnite has] done something that's really unique, which is come up with a perception of exclusivity." He added, "If you see another player in a leopard skin and go to the store and see it's no longer available, you think, Shoot, I've got to move on it next time."
All three complainants are represented by the law firm Pierce Bainbridge Beck Price & Hecht LLP. In addition to copyright infringement, the lawsuits allege violations of the rights to publicity, which are creators' rights to control and profit off any use of their likeness, name, or other distinct traits. David L. Hecht, the representative for 2 Milly, Ribeiro, and Horning, insists that his clients have exclusive rights to the cultural trends they've instigated, stating, "I will say you can absolutely copyright choreography, and you can leave it there." Whether U.S. law is in agreement with him is for a judge to decide in 2019.
Meg Hanson is a Brooklyn-based writer, teacher, and jaywalker. Find Meg at her website and on Twitter @megsoyung.
- 'Fortnite' maker Epic Games may face more lawsuits for dance moves ›
- A Real-World Battle Over Dancing Avatars: Did Fortnite Steal the ... ›
- Fortnite sued over The Floss: Can you copyright a dance move ... ›
- Celebrities suing 'Fortnite' over dance moves - CNN Video ›
- Fortnite Dance Lawsuits: What's The Story Behind Them? | Billboard ›
- Real-Life Lawyer Shares Insight on Fortnite Dance Move Lawsuits ›
- 'Fortnite' Dance Lawsuits: Carlton, Floss, Milly Rock Copyrightable ... ›
- How Fortnite's dance moves sparked new lawsuits against Epic ... ›
- The Fortnite Dance Lawsuits Are Super Important (Seriously ... ›
- Epic and Fortnite's dance lawsuits - Polygon ›